
Authors: Conor Delaney, Valerie McCarthy, Kevin French, Sita Karki, Vicky Veerkamp, Moataz Ahmed Abdel Ghaffar, Jenny Hanafin, Alastair McKinstry, Eleanor Jennings and Aaron Golden, November 2023
Year: 2023
Lakes, estuaries, and coastal waters are crucial for human well-being. Lakes are critical sources of drinking water, and support irrigation, fisheries, and aquaculture activities. These waters are also important for recreation and tourism and support high levels of biodiversity. The number and diversity of water bodies in Ireland makes regular in situ monitoring an acute challenge for regulatory authorities. Ireland has legally binding legislative obligations under the WFD. This project determined if the use of freely available Earth observation data from both the Copernicus and Landsat Earth observation programmes could offer a cost-effective and evidence-based means of remotely monitoring such water bodies in Ireland.

Authors: Aonghus Ó Domhnaill, Margaret O’Mahony, Brian Broderick, Martina Hennessy, Aoife Donnelly, Owen Naughton, Eimir Hurley, Philip Carthy, Anne Nolan, Frank Moriarty and Seán Lyons, November 2023
Year: 2023
Exposure to nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is associated with adverse effects on hospital admissions for various diagnoses; respiratory illnesses such as asthma, cancer, adverse birth outcomes, as well as mortality. The main source of NO2 in Ireland is road transport, particularly diesel engines. Other sources include off-road machinery, industrial and construction activities, and electricity and heat production. This research project analysed associations between the model estimations of NO2 and the health data of 8000 adults aged over 50 years. Using the HSE-PRCR prescribing database, the project found a positive association between respiratory item prescription rates and PM2.5 levels, while the results for NO2 were inconclusive. The project also developed an enhanced Wind Sector Land Use Regression (WS-LUR) model that estimates ambient NO2 concentrations at any location in Ireland with particular emphasis on vehicle fleet changes and traffic flow impacts on NO2.

Authors: Jane C. Stout, Catherine A. Farrell, Mary Kelly-Quinn, Lisa Coleman,Stephen Kinsella, Cathal O’Donoghue, Daniel Norton, Carl Obst, Mark Eigenraam,Fiona Smith, Iseult Sheehy and Sarah Zimmermann., November 2023
Year: 2023
Nature continues to be degraded globally. Despite our societies and economies depending on it, we often ignore or undervalue this degradation. To bring nature into everyday decision-making, the natural capital approach deliberately uses the language of business and economics. In this context, nature can be thought of as an array of stocks of natural assets, incorporating biodiversity, air, water and geology. The condition of these stocks influences the flow of goods and services, and the benefits that our societies and economies derive from these assets. This EPA Research Report provides insights into the development of natural capital accounts at the catchment scale in Ireland. It aims to provide a comprehensive view of the stocks of natural capital assets and the flows of services, along with guidance on how to scale-up the process to national level.

Authors: Bart Bonsall, Donncha Haverty, Corine Nzeteu, Pádraic Ó hUiginn and Vincent O’Flaherty, November 2023
Year: 2023
Across the EU, anthropogenic sources of nitrogen (N) threaten water and air quality. Agriculture is also a significant source of N and GHG emissions linked to climate change. N for crops is sourced from mineral fertilisers, livestock manures and anaerobic digestion digestates. Landfill leachates also generate N and GHG emissions. The EPA funded this research to identify cost-effective methods to mitigate the release of N and GHGs from ammoniacal streams.

Authors: Ylva Andersson, Peter Barlow, Philip Carthy, Kelly de Bruin, Míde Griffin, Seán Lyons, Pete Lunn, Bertrand Maître, Likun Mao, Maria Martinez Cillero, David Meier, Gretta Mohan, Kieran Mohr, Anne Nolan, Brian O’Connell, Vincent O’Sullivan, Aidan Sloyan, Shane Timmons, Miguel Tovar Reaños, Brendan Walsh and Aykut Mert Yakut, October 2023
Year: 2023
The main objective of this EPA-ESRI collaboration is to produce policy-relevant applied research at the interface between the environment, economy, and society. This report provides a summary of 12 studies, produced by the ESRI, that use a range of data and methodological approaches to provide insights into the environmental challenges facing Irish society. The studies include analyses of the impact on healthcare systems from the smoky coal ban, living in areas of higher PM2.5 levels, e-coli exceedances in drinking water and water related diseases in the summer months. It also examines the potential for a “green VAT”, the levels of emissions embedded in imports and the best ways to present information to people to enable action.

Authors: Zane Ferch, Steve Coughlan, Charlotte O’Kelly and Sinead McGlynn, October 2023
Year: 2023
This research provides enforcement authorities with viable options to use cost effective technological tools to quickly detect and react to industrial and waste crime.

Authors: Jonathan Yearsley, Rainer Melzer and Carl Frisk, September 2023
Year: 2023
Agricultural grasslands are a crucial part of Ireland’s agroeconomy. Within these grasslands, perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) is the dominant species and underpins much of their performance, of which the timing of growth (i.e., the phenology of grasslands) is an important aspect. A late start or an early end to the growing season requires grazing livestock to be housed for longer, which in turn requires farmers to have additional reserves of forage. Reserves depend on the length of the grass growing season. Seasons with exceptionally late starts and those with poor forage harvests have been major contributory factors to past fodder crises, with broad consequences for the economy, animal welfare and human well-being.

Liz Coleman and Frank McGovern, August 2023
Year: 2023
The impact of human activity since the Industrial Revolution has altered the environment, pushing its stability to critical limits, with real implications for societal, economic and environmental systems. The planetary boundaries framework has provided a powerful tool for communicating the individual and collective threats arising from unsustainable post-industrial development, yet actions and responses take place at regional, national and local levels.

Authors: Colm Gaskin, Ken Stockil, Thomas Track, William Horan, Andres Lucht and Paul Conheady, July 2023
Year: 2023
Industrial activity is intrinsically linked to the accessibility and availability of water. The increasing global demand for industrial water poses a significant risk management challenge for organisations aiming to decouple the growth of production capacity from unsustainable consumption. This report presents a framework for industrial water users to adopt Industrial Water 4.0.

Year: 2023
The EPA organised an inaugural Environmental Science to Policy Seminar in October 2022. Its objective was to explore how best to improve the delivery of evidence and knowledge to the policymaking system. The event brought together policymakers, knowledge transfer practitioners and scientists from across government and academia to share experiences on the issues, constraints, good practices and ways forward. This Seminar Reflections Paper captures the key themes and recommendations that emerged during the seminar, to support and inform the national Science to Policy agenda.

Authors: Stuart Harrad, Martin Sharkey, D.aniel Drage, William Stubbings, Marie Coggins and Harald Berresheim, June 2023
Year: 2023

Authors: Robert J. Forster, June 2023
Year: 2023
Many wastewater streams, such as those from the pharmaceutical and food industries or from municipal wastewater, for example, contain pollutants. The SPy project developed the eco-innovative ‘Sense and Purify’ (SPy) technology, which has significant advantages over traditional treatment processes, including low operations costs, significantly lower energy consumption, higher conversion efficiency, better effluent water quality and lower waste production.
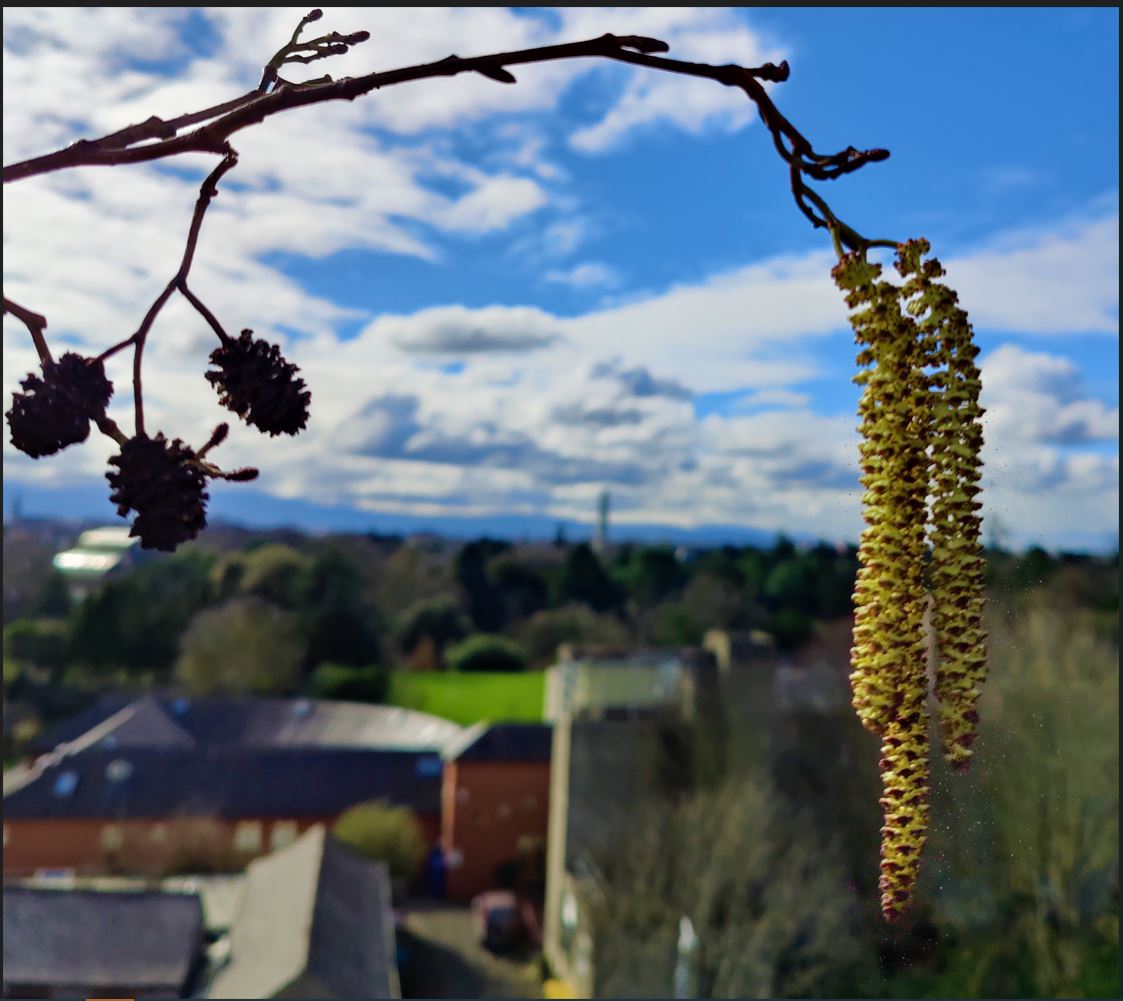

Pollen over Dublin City: Urban Exposure , May 2023
Year: 2023
Ireland has one of the highest incidents rates of asthma in the world with 80% of Irish asthmatics also possessing pollen allergies. Therefore, airborne pollen represents and immediate respiratory risk to the Irish public, especially for those in urban areas. The Irish monitoring network has only very recently commenced tracking the airborne pollen. Previously only broad inaccurate forecasts made in the UK were available. This entry represents the hard work that has gone into establishing a pollen monitoring network. The image was taken atop the Met Éireann facility, showing a pollen catkin against the city back-drop, with O’Connell tower seen piercing the sky. The image was taken on the day the first pollen sampler was installed there. Since then, we have continued to monitor pollen in Dublin and at several other sites with the hopes of continuing and improving the network and sharing results with those that need it.
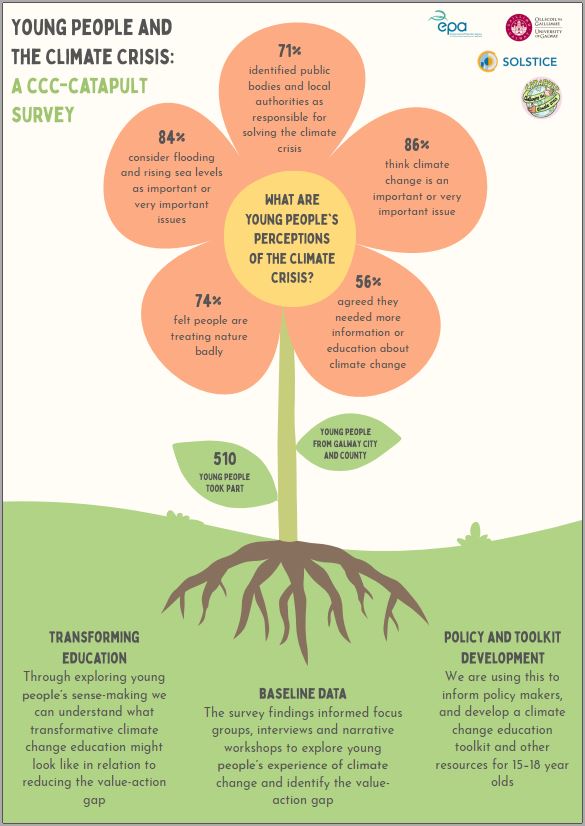
CATAPULT Survey Infographics, May 2023
Year: 2023
Details of a unique survey questioning 15 – 18 year olds in Galway city and Galway county schools on their experiences of climate change and the climate crisis. Survey undertaken not only in Ireland but in three other European countries, UK, Finland and Italy also with nearly 2000 young people aged between 15 – 18 years of age participating. One of the outcomes of this online survey was generation of baseline data set for Focus Groups, Interviews and Narrative Workshops. Another outcome of the survey to inform stakeholders and policy makers, and facilitate in the production of a Climate Change Education Toolkit and resources for both formal and informal educational settings.

Authors: Jessica Graça, Brian Murphy and Brian Kelleher, May 2023
Year: 2023
The EPA’s latest data (November 2022) show that municipal waste generation increased by over 440,000 tonnes in the last 5 years, and now amounts to 3.2 million tonnes. The VALOR study looked at how the resource value of the mechanically separated organic fraction of municipal solid waste (MS-OFMSW) can be maximised. The study also characterised the organic fractions of municipal solid waste (MSW).